Managing remote desktop connections in a world where IoT devices are increasingly common can be both challenging and rewarding. Whether you're working from home, running a small business, or managing a large enterprise, understanding how to configure an IoT remote desktop behind NAT on Mac is essential for modern computing needs.
As technology continues to evolve, remote access has become a critical component of productivity. For Mac users, setting up IoT remote desktop solutions behind NAT offers flexibility and efficiency. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to help you navigate through the complexities of configuring such systems, ensuring seamless connectivity and enhanced performance.
Whether you're a beginner or an experienced IT professional, this guide is designed to address your questions, provide actionable steps, and offer expert insights into IoT remote desktop configurations. Let's dive in and unlock the potential of your Mac-based IoT setup.
Read also:Who Is Kathleen Quinlan Unveiling The Life And Career Of A Hollywood Icon
Table of Contents
- Introduction to IoT Remote Desktop Behind NAT
- Understanding IoT and Its Role in Remote Access
- What is NAT and Why It Matters
- Setting Up Remote Desktop on Mac
- Configuring NAT for IoT Devices
- Essential Tools for Managing IoT Remote Desktop
- Enhancing Security for IoT Remote Desktop
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Best Practices for Efficient IoT Remote Desktop Management
- Future Trends in IoT Remote Desktop Technology
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to IoT Remote Desktop Behind NAT
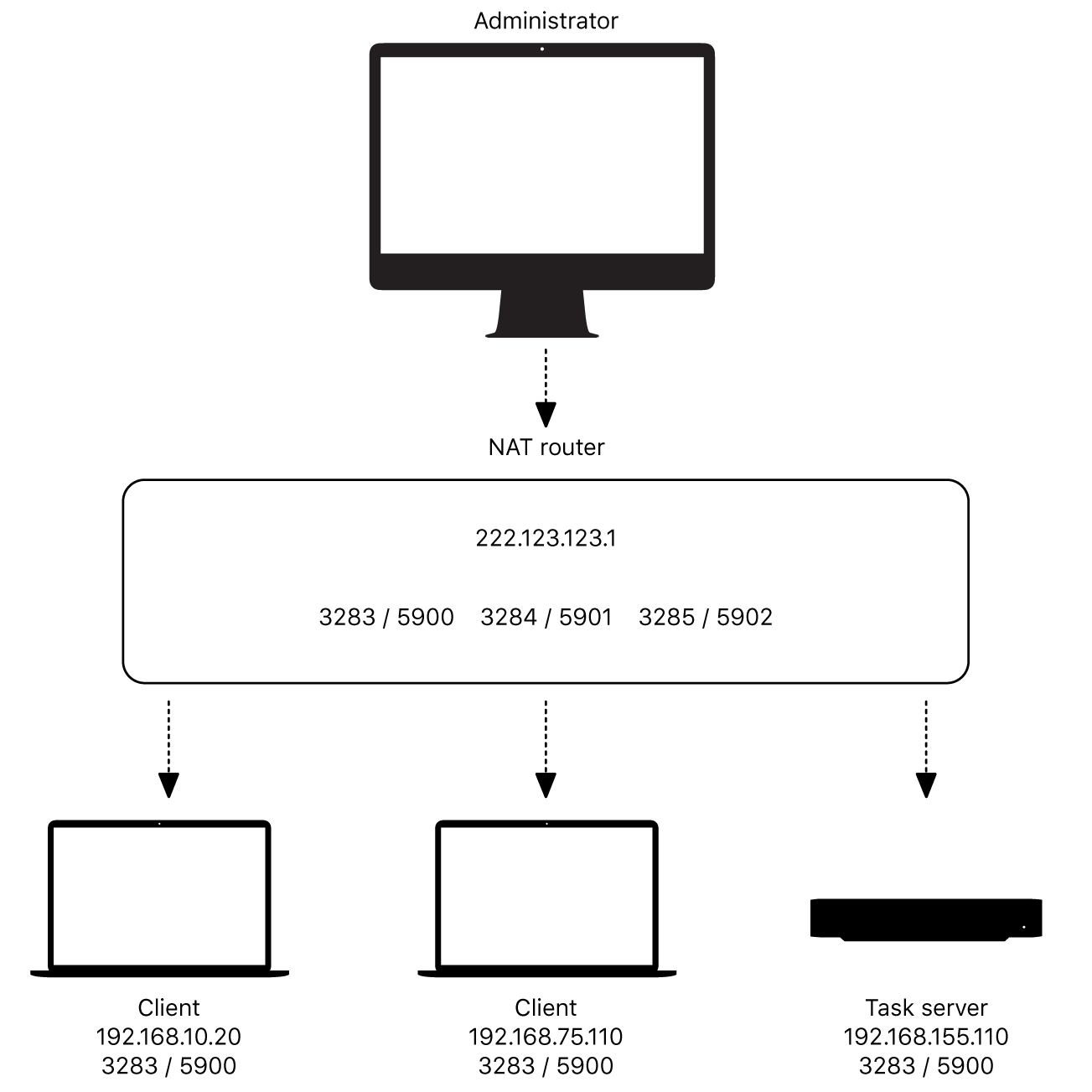
Remote desktop technology has revolutionized the way we work, especially in the context of IoT. For Mac users, setting up a remote desktop behind NAT ensures secure and reliable access to IoT devices from anywhere. This section will introduce you to the basics of IoT remote desktop configurations and explain why NAT plays a crucial role in modern networking environments.
In simple terms, NAT (Network Address Translation) allows multiple devices within a local network to share a single public IP address. This is particularly important for IoT setups where numerous devices need to communicate with external networks. By understanding how NAT works, you can optimize your remote desktop experience and ensure smooth connectivity.
Understanding IoT and Its Role in Remote Access
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of interconnected devices capable of collecting and exchanging data. From smart thermostats to industrial sensors, IoT devices are transforming industries by enabling real-time monitoring and automation.
IoT and Remote Desktop
Integrating IoT devices into remote desktop environments offers numerous advantages. It allows administrators to monitor and control devices remotely, improving efficiency and reducing downtime. For Mac users, leveraging IoT for remote desktop purposes requires a solid understanding of network configurations and security protocols.
- IoT enhances remote access capabilities.
- Smart devices can be managed from anywhere.
- Automation reduces manual intervention.
What is NAT and Why It Matters
NAT (Network Address Translation) is a networking technique that enables multiple devices within a local network to share a single public IP address. This is particularly useful in scenarios where numerous IoT devices need to connect to the internet without requiring unique public IP addresses for each device.
In the context of remote desktop configurations, NAT simplifies the process of accessing IoT devices from external networks. By translating private IP addresses into a single public IP, NAT ensures that communication between devices remains seamless and secure.
Read also:Vital Information About The United States Department Of Health And Human Services
Setting Up Remote Desktop on Mac
Enabling Remote Management on macOS
macOS provides built-in support for remote desktop connections through the Screen Sharing feature. To enable remote access:
- Go to System Preferences > Sharing.
- Select "Screen Sharing" and check the box to enable it.
- Add users who are allowed to connect remotely.
Connecting to a Remote Mac
To connect to a remote Mac, you can use the Finder application or third-party tools like TeamViewer or AnyDesk. Ensure that both devices are on the same network or configure port forwarding if accessing from outside the local network.
Configuring NAT for IoT Devices
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is a common technique used to configure NAT for IoT remote desktop setups. By directing specific ports to individual devices, you can ensure that incoming connections reach the correct IoT device. Follow these steps:
- Log in to your router's admin panel.
- Navigate to the "Port Forwarding" section.
- Specify the port number and the internal IP address of the IoT device.
Dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) services can help maintain consistent access to IoT devices even when your public IP address changes. By linking your IP address to a domain name, you can access your devices using a memorable URL instead of an IP address.
Essential Tools for Managing IoT Remote Desktop
Several tools are available to simplify IoT remote desktop management on Mac. Some popular options include:
- TeamViewer: A versatile remote desktop solution with robust security features.
- AnyDesk: Known for its speed and efficiency, AnyDesk is an excellent choice for IoT remote access.
- VNC Viewer: A lightweight tool that supports various VNC-based protocols.
When selecting a tool, consider factors such as ease of use, compatibility with IoT devices, and security features.
Enhancing Security for IoT Remote Desktop
Encryption
Encrypting data transmissions is critical for securing IoT remote desktop connections. Use protocols like SSL/TLS to ensure that sensitive information remains protected during transmission.
Two-Factor Authentication
Implementing two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to your remote desktop setup. This ensures that unauthorized users cannot gain access to your IoT devices, even if they manage to obtain your login credentials.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful planning, issues can arise when configuring IoT remote desktop setups. Below are some common problems and their solutions:
- Connection Failures: Verify that port forwarding is correctly configured and that firewalls are not blocking incoming connections.
- Slow Performance: Optimize network settings and ensure that your internet connection meets the requirements for remote desktop usage.
- Security Alerts: Regularly update software and firmware to address potential vulnerabilities.
Best Practices for Efficient IoT Remote Desktop Management
To maximize the benefits of IoT remote desktop configurations, consider adopting the following best practices:
- Regularly back up important data to prevent loss in case of connectivity issues.
- Monitor network performance and adjust settings as needed to ensure optimal speed and reliability.
- Document your configurations and share them with team members to streamline troubleshooting processes.
Future Trends in IoT Remote Desktop Technology
As technology continues to advance, the future of IoT remote desktop management looks promising. Emerging trends such as AI-driven automation, enhanced encryption protocols, and cloud-based solutions are set to transform the way we interact with IoT devices. Staying informed about these developments will help you stay ahead of the curve and make the most of your IoT setup.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, configuring an IoT remote desktop behind NAT on Mac requires a combination of technical knowledge, strategic planning, and attention to detail. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can create a secure and efficient remote access environment that meets your needs.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into IoT and remote desktop technologies. Together, let's build a smarter, more connected future!
Data and references for this article were sourced from reputable publications such as Cisco, Apple, and Microsoft.