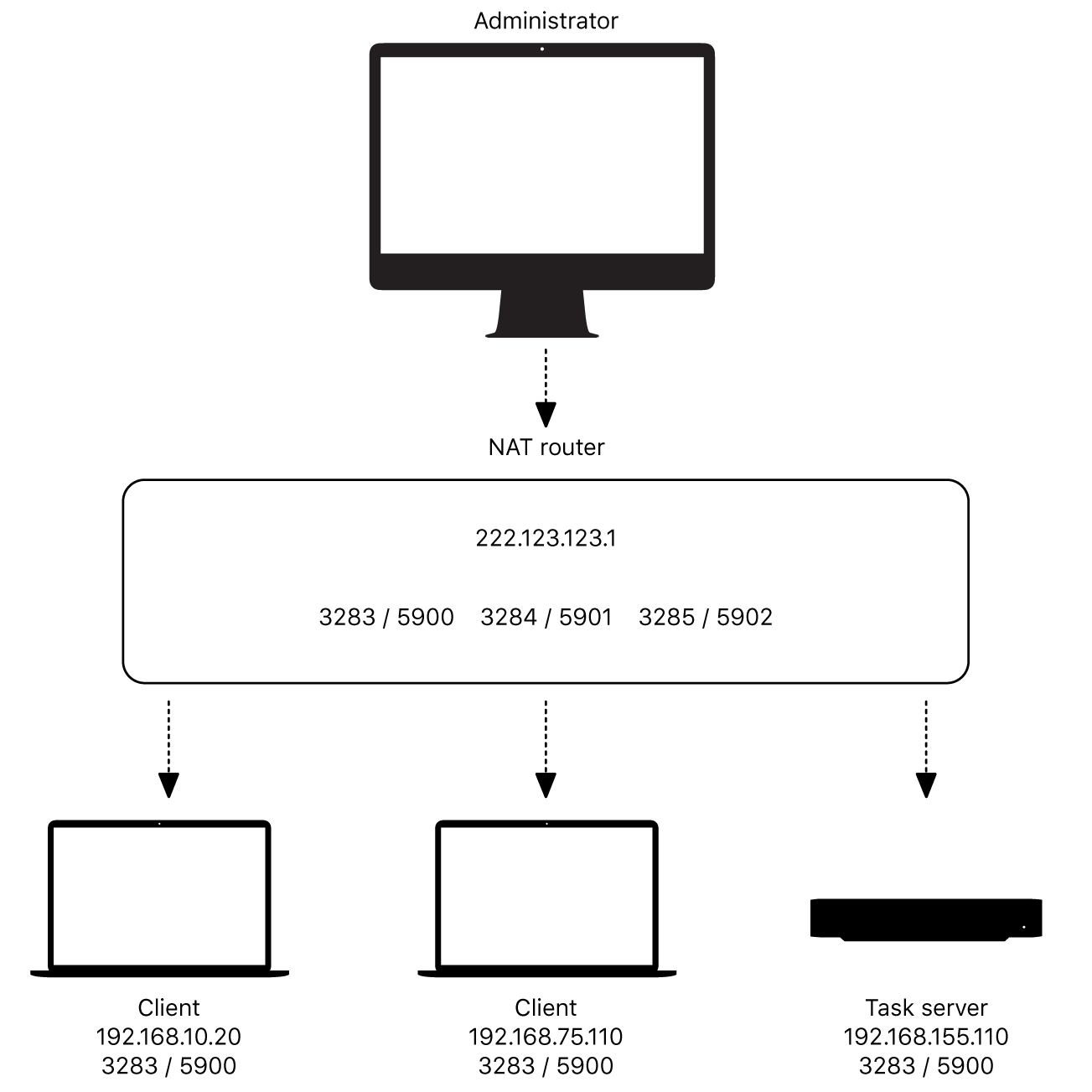
In today's interconnected world, IoT remote desktop behind NAT has become a critical solution for businesses and individuals alike. The ability to access devices remotely, even when behind a Network Address Translation (NAT) layer, opens up new possibilities for productivity and convenience. However, understanding the complexities of NAT traversal and remote desktop protocols can be daunting for many users.
This article dives deep into the concept of IoT remote desktop behind NAT, exploring its applications, challenges, and solutions. Whether you're a tech enthusiast or a professional looking to enhance your remote access capabilities, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and tools you need to succeed.
By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how to set up and manage IoT remote desktop connections, even in complex network environments. Let's get started!
Read also:Martin Dugger Elk City Ok A Comprehensive Guide To His Life Career And Impact
Table of Contents
- Introduction to IoT Remote Desktop Behind NAT
- What is NAT and Why Does It Matter?
- Understanding IoT Remote Desktop
- Challenges of IoT Remote Desktop Behind NAT
- Solutions for NAT Traversal
- Tools and Software for IoT Remote Desktop
- Security Considerations for IoT Remote Access
- Optimizing IoT Remote Desktop Performance
- Future Trends in IoT Remote Desktop
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to IoT Remote Desktop Behind NAT
The concept of IoT remote desktop behind NAT has gained significant traction in recent years. As more devices become connected to the internet, the need for secure and efficient remote access solutions has grown exponentially. NAT, or Network Address Translation, plays a crucial role in enabling multiple devices to share a single public IP address, but it also poses challenges for remote access.
Why IoT Remote Desktop is Essential
IoT remote desktop allows users to access and control devices remotely, enabling them to perform tasks such as troubleshooting, monitoring, and managing IoT systems. This capability is especially valuable in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and telecommunications, where real-time access to devices is critical.
However, when devices are behind NAT, establishing a secure and reliable connection can be challenging. This article will explore the intricacies of NAT traversal and provide practical solutions for overcoming these obstacles.
What is NAT and Why Does It Matter?
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a networking technology that enables multiple devices on a private network to share a single public IP address. NAT works by translating private IP addresses into a public IP address when communicating with external networks. This process is essential for conserving IPv4 addresses and enhancing network security.
Types of NAT
- Static NAT: Maps a single private IP address to a single public IP address.
- Dynamic NAT: Maps multiple private IP addresses to a pool of public IP addresses.
- Port Address Translation (PAT): Also known as NAT overload, PAT allows multiple devices to share a single public IP address by assigning unique port numbers to each connection.
Understanding the different types of NAT is crucial for implementing effective remote desktop solutions in NAT environments.
Understanding IoT Remote Desktop
An IoT remote desktop solution enables users to access and control IoT devices from a remote location. This technology leverages protocols such as RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol), VNC (Virtual Network Computing), and SSH (Secure Shell) to establish secure connections between devices.
Read also:Discover The Legacy Of Landmark Century Center A Mustvisit Destination
Key Features of IoT Remote Desktop
- Remote Access: Allows users to access devices from anywhere in the world.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Provides real-time data and insights into device performance.
- Secure Connections: Ensures data privacy and protection through encryption and authentication mechanisms.
When combined with NAT traversal techniques, IoT remote desktop solutions can overcome the limitations imposed by private networks.
Challenges of IoT Remote Desktop Behind NAT
While IoT remote desktop offers numerous benefits, implementing this technology in NAT environments presents several challenges. These include:
- Address Translation: Devices behind NAT have private IP addresses that are not directly accessible from the internet.
- Firewall Restrictions: Firewalls and security policies can block incoming connections, making it difficult to establish remote sessions.
- Latency: High network latency can impact the performance of remote desktop connections, especially in complex NAT setups.
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive understanding of NAT traversal techniques and remote desktop protocols.
Solutions for NAT Traversal
To overcome the challenges of IoT remote desktop behind NAT, several solutions have been developed. These include:
UPnP (Universal Plug and Play)
UPnP is a protocol that allows devices to automatically configure port forwarding on routers, enabling direct connections to devices behind NAT. While UPnP simplifies the setup process, it can pose security risks if not properly configured.
STUN (Session Traversal Utilities for NAT)
STUN is a protocol that helps devices discover their public IP address and determine the type of NAT they are behind. By using STUN servers, devices can establish peer-to-peer connections, even when behind NAT.
Relay Servers
Relay servers act as intermediaries between devices, forwarding data packets between them. This approach ensures reliable connections, even in complex NAT environments, but can introduce additional latency.
By leveraging these technologies, users can establish secure and efficient IoT remote desktop connections, even when devices are behind NAT.
Tools and Software for IoT Remote Desktop
Several tools and software solutions are available for implementing IoT remote desktop behind NAT. Some popular options include:
- TeamViewer: A versatile remote desktop solution that supports NAT traversal and provides robust security features.
- AnyDesk: A fast and secure remote desktop tool that offers seamless connectivity, even in complex network environments.
- ngrok: A tunneling service that allows users to expose local servers to the internet, making it easier to access devices behind NAT.
Each of these tools has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it's important to evaluate your specific needs before selecting a solution.
Security Considerations for IoT Remote Access
When implementing IoT remote desktop behind NAT, security should be a top priority. Key considerations include:
Authentication
Implementing strong authentication mechanisms, such as two-factor authentication (2FA), can help protect against unauthorized access.
Encryption
Using encryption protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) ensures that data transmitted between devices remains confidential and secure.
Firewall Configuration
Configuring firewalls to allow only necessary traffic can reduce the risk of cyberattacks and unauthorized access.
By addressing these security considerations, users can ensure the safety and integrity of their IoT remote desktop connections.
Optimizing IoT Remote Desktop Performance
To maximize the performance of IoT remote desktop behind NAT, several optimization techniques can be applied. These include:
- Compressing data to reduce bandwidth usage.
- Using low-latency protocols to minimize delays.
- Optimizing network configurations to improve connection stability.
Implementing these techniques can enhance the user experience and ensure reliable remote access, even in challenging network conditions.
Future Trends in IoT Remote Desktop
The field of IoT remote desktop is rapidly evolving, with new technologies and innovations emerging regularly. Some key trends to watch include:
5G Networks
The rollout of 5G networks promises to revolutionize remote access by providing faster speeds and lower latency, enabling more efficient IoT remote desktop solutions.
AI-Powered Optimization
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to optimize remote desktop performance by analyzing network conditions and adjusting settings in real time.
Quantum Encryption
As quantum computing becomes more prevalent, quantum encryption technologies are being developed to enhance the security of remote desktop connections.
Staying informed about these trends will help users stay ahead of the curve and take full advantage of the latest advancements in IoT remote desktop technology.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, IoT remote desktop behind NAT offers powerful capabilities for accessing and managing devices remotely. By understanding the challenges and solutions associated with NAT traversal, users can implement secure and efficient remote access solutions that meet their specific needs.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore our other articles for more insights into IoT and remote desktop technologies. Together, let's shape the future of connected devices and remote access!
Data Sources: