Are you struggling with IoT remote desktop behind NAT not working? Don't worry, you're not alone. Many users encounter this issue when trying to access their IoT devices remotely through a NAT (Network Address Translation) network. This problem can be frustrating, especially when you need seamless connectivity for work or personal use. In this article, we'll explore the root causes and provide actionable solutions to help you resolve this issue.
As more businesses and individuals adopt IoT technology, the demand for remote access has increased significantly. However, challenges like NAT traversal can hinder the smooth functioning of IoT remote desktop setups. Understanding the underlying causes and implementing the right solutions can save you time and effort.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll cover everything from basic troubleshooting steps to advanced configurations. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced IT professional, this article will equip you with the knowledge to resolve IoT remote desktop connectivity issues behind NAT networks.
Read also:Discover Where To Find The Beloved Little Angels Cream
Table of Contents
- Introduction to IoT Remote Desktop
- Understanding NAT Traversal
- Common Issues with IoT Remote Desktop Behind NAT
- How to Diagnose the Problem
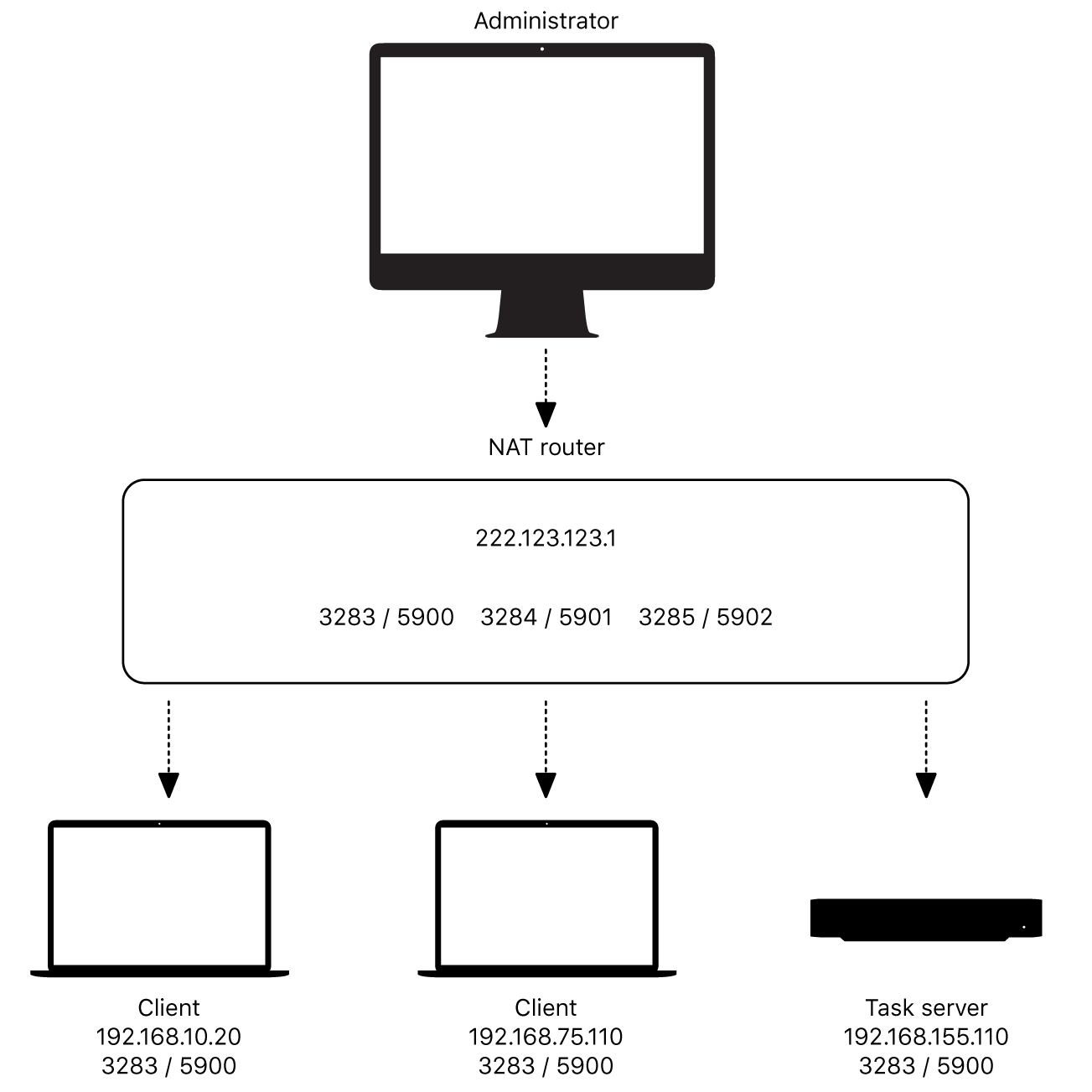
- Port Forwarding as a Solution
- Using VPN for NAT Traversal
- Enabling UPnP for Seamless Connectivity
- Software Tools for Troubleshooting
- Advanced Configuration Techniques
- Best Practices for IoT Remote Desktop
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to IoT Remote Desktop
IoT remote desktop technology allows users to access and control IoT devices remotely from anywhere in the world. This functionality is essential for managing smart home devices, industrial equipment, and other connected systems. However, when these devices are behind a NAT network, connectivity issues may arise.
NAT is a networking technology that enables multiple devices to share a single public IP address. While NAT enhances security and conserves IP addresses, it can also create barriers for remote access. Understanding how NAT works and its impact on IoT remote desktop connectivity is crucial for troubleshooting and resolving issues.
Understanding NAT Traversal
What is NAT Traversal?
NAT traversal refers to the process of enabling communication between devices located in different private networks through a NAT gateway. This is particularly important for IoT remote desktop applications, as they often require inbound connections to devices behind NAT.
Several techniques can be used for NAT traversal, including:
- Port forwarding
- UPnP (Universal Plug and Play)
- STUN/TURN servers
- VPN tunnels
Common Issues with IoT Remote Desktop Behind NAT
When IoT remote desktop connections fail behind NAT, the problem is often related to network configuration. Some common issues include:
- Incorrect port forwarding settings
- Firewall blocking inbound connections
- UPnP not enabled on the router
- Incompatible NAT types
Each of these issues requires a specific approach to resolve. Identifying the root cause is the first step toward finding an effective solution.
Read also:Peachy Cat Snack The Ultimate Delight For Your Furry Friend
How to Diagnose the Problem
Diagnosing IoT remote desktop connectivity issues involves several steps. Start by checking the following:
- Router settings: Ensure that port forwarding is correctly configured.
- Firewall rules: Verify that the firewall is not blocking necessary ports.
- Network topology: Map your network to identify potential bottlenecks.
- Device logs: Review logs from your IoT devices for error messages.
Using diagnostic tools like ping, traceroute, and netstat can also help pinpoint connectivity issues.
Port Forwarding as a Solution
What is Port Forwarding?
Port forwarding is a technique that allows inbound traffic to reach a specific device on a private network. By mapping external ports to internal IP addresses, you can enable remote access to IoT devices behind NAT.
To set up port forwarding:
- Log in to your router's admin interface.
- Locate the port forwarding settings.
- Specify the external port and map it to the internal IP address of your IoT device.
- Save the configuration and test the connection.
Using VPN for NAT Traversal
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) provide a secure and reliable way to bypass NAT restrictions. By creating a tunnel between your IoT device and the remote client, a VPN ensures seamless connectivity regardless of NAT configuration.
Popular VPN solutions for IoT remote desktop include:
- OpenVPN
- WireGuard
- ZeroTier
Choose a VPN protocol that balances security, speed, and ease of use based on your requirements.
Enabling UPnP for Seamless Connectivity
What is UPnP?
UPnP is a networking protocol that allows devices to automatically configure port forwarding without manual intervention. Enabling UPnP on your router can simplify the setup process for IoT remote desktop applications.
To enable UPnP:
- Access your router's admin interface.
- Find the UPnP settings and toggle it on.
- Restart your router to apply the changes.
Keep in mind that UPnP may pose security risks if not properly configured. Ensure that your router firmware is up to date and consider using additional security measures.
Software Tools for Troubleshooting
Several software tools can assist in diagnosing and resolving IoT remote desktop connectivity issues. Some recommended tools include:
- Wireshark: A network protocol analyzer for capturing and analyzing traffic.
- Advanced IP Scanner: A utility for discovering devices on your network.
- Port Checker: A tool for verifying if specific ports are open and accessible.
Using these tools can help you identify and resolve connectivity problems more efficiently.
Advanced Configuration Techniques
Configuring STUN/TURN Servers
STUN (Session Traversal Utilities for NAT) and TURN (Traversal Using Relays around NAT) servers are specialized tools designed to facilitate NAT traversal. By deploying these servers, you can improve the reliability of IoT remote desktop connections.
Steps to configure STUN/TURN servers:
- Select a suitable STUN/TURN server provider or set up your own server.
- Integrate the server into your IoT application's configuration.
- Test the connection to ensure proper functionality.
Best Practices for IoT Remote Desktop
To ensure optimal performance and security for IoT remote desktop applications, follow these best practices:
- Regularly update firmware and software for all devices involved.
- Use strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication where possible.
- Monitor network activity for signs of unauthorized access.
- Document your network configuration for easy reference.
Implementing these practices can help you maintain a secure and reliable IoT remote desktop setup.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, resolving IoT remote desktop connectivity issues behind NAT requires a systematic approach. By understanding the underlying causes and applying the right solutions, you can achieve seamless remote access to your IoT devices. Whether you choose port forwarding, VPNs, or UPnP, each method has its advantages and limitations.
We encourage you to share your experiences and tips in the comments below. Your feedback helps us improve and provides valuable insights for other readers. Additionally, explore our other articles for more tips on IoT and networking solutions.
Stay connected and keep troubleshooting!